Nutrient availability: the foundational driver of sustainable agricultural ecosystems
In a global agricultural landscape where growers must increase productivity while reducing external inputs, nutrient availability has emerged as the cornerstone of sustainable and regenerative farming.
Nutrient availability refers to the processes that determine how much of the soil’s nutrient pool is actually accessible to plants. It is the biological engine that sustains soil fertility, enhances crop vigor, and minimizes reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
Excessive use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides contributes to nutrient leaching, soil degradation, and water pollution, issues that weaken ecosystem resilience and reduce profitability. Globally, around one-third (approximately 30–33%) of soils are moderately to highly degraded due to factors including nutrient depletion, erosion, salinization and compaction which strip away nutrient-rich topsoil and diminish the nutrient availability needed for plant growth and soil biological activity.
Policy frameworks such as the EU Farm to Fork Strategy and the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) reinforce the shift toward nutrient‑efficient, climate‑smart agriculture, encouraging practices that enhance nutrient cycling, nutrient availability, and nutrient use efficiency (NUE) while reducing dependency on synthetic agrochemicals.
Nutrient cycling: the biological engine keeping nutrients in motion
Nutrient cycling refers to the continuous set of transformations through which nutrients are released, mobilized, stabilized, and reused within the soil–plant–microorganism system. It encompasses key processes such as:
- organic matter mineralization
- microbial decomposition
- biological nitrogen fixation
- phosphorus solubilization
- potassium mobilization
When these processes function effectively, nutrients flow into plant‑available forms, enhancing soil fertility without depending on excessive synthetic fertilizer inputs.
Enhancing nutrient cycling in agriculture
Several regenerative practices are especially powerful to boost nutrient cycling. They include:
- Cover crops. Cover crops protect the soil’s surface, add organic carbon, and stimulate microbial activity.
- Compost and organic amendments. These amendments increase organic matter and improve soil structure.
- Microbial inoculants. These inoculants enhance decomposition, fixation, and nutrient solubilization.
- Agroforestry and increased plant diversity. This creates more complex and resilient soil food webs.
These strategies enrich soil quality, reduce nutrient losses through leaching and volatilization, and keep nutrient cycles active even under climatic stress.
Nutrient use efficiency: the functional core of a sustainable farming ecosystem
Nutrient use efficiency (NUE) represents the integrated capacity of the soil–plant–microorganism system to mobilize, transform, and utilize essential elements such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with minimal losses. In regenerative agriculture, NUE and nutrient availability operate as a single, continuous process in which nutrients are released, stabilized, and taken up through closely linked biogeochemical pathways.
Key mechanisms include:
- root system architecture and exploration
- microbial activity in the rhizosphere
- nutrient assimilation pathways
- soil pH and chemical balance
- plant physiological efficiency under stress
The synergy: when nutrient cycling and NUE work together
When nutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency operate synergistically, agricultural systems become:
- more resilient,
- more resource‑efficient,
- more carbon‑efficient,
- less dependent on synthetic inputs,
- and more capable of sustaining long‑term productivity.
The activation of soil microbial communities, combined with regenerative practices, transforms farmland into a continuous biological engine that releases, transforms, and recycles nutrients naturally. This synergy enables growers to maintain and even increase yields while reducing input costs and minimizing environmental impact.
These management strategies enable agroecosystems to operate more efficiently, maintain productivity with fewer external inputs, and build resilience against environmental stressors by strengthening the biological foundations that simultaneously govern nutrient cycling and NUE.
Benefits for growers and agricultural stakeholders
Enhancing nutrient cycling and nutrient use efficiency delivers both economic and agronomic benefits. These include:
- Reduced dependence on synthetic fertilizers
- Improved root absorption capacity and nutrient capture efficiency
- Better soil structure and water‑holding capacity
- Lower nutrient leaching and volatilization
- Maintained or increased yield with fewer inputs
These advantages support the transition toward low‑input, high‑performance farming systems that are more sustainable and profitable.
Biosolutionize Agriculture: activating nutrient availability and NUE through Rovensa Next
Rovensa Next’s holistic biosolutions portfolio is designed to activate soil biology, enhance nutrient cycling availability, and increase nutrient use efficiency. Its solutions include:
- Bionutrition products (specialty crop nutrition, biostimulants, biofertilizers)
- Biocontrol products (biofungicides, bioinsecticides, bionematicides, plant growth regulators (PGR))
- Adjuvants (activator adjuvants, utility adjuvants, soil conditioners, specialty adjuvants, multi‑function adjuvants).
These categories directly target mechanisms such as biological nitrogen fixation, phosphorus solubilization, potassium mobilization, mineralization, root stimulation, and nutrient uptake improvement, which are key processes in achieving sustainable crop nutrition, soil vitality, and regenerative outcomes.
How Biostimulation 360º enhances nutrient availability & nutrient use efficiency (NUE)
- Plant-level NUE: improving nutrient uptake, mobility, and translocation
Beyond the soil, Biostimulation 360° also elevates nutrient use efficiency by enhancing the plant’s internal nutrient transport and metabolic performance during growth stages with high nutrient demand. Biostimulants which are rich in L‑α free amino acids, such as Delfan Plus and Vegenergy, promote rapid nutrient translocation to developing organs, improve calcium mobility in apples, and help prevent physiological disorders such as Bitter Pit. Meanwhile, the Phylgreen range, based on cold‑extracted Ascophyllum nodosum, activates plant metabolism and strengthens nutrient absorption under stress conditions, optimizing the use of elements such as boron in nutrient‑sensitive crops, including canola and legumes. Together, these solutions help crops to overcome physiological limitations in uptake and mobilization, delivering higher productivity with fewer inputs, and significantly improving overall NUE.
- Soil-level NUE: enhancing nutrient availability and root efficiency
Within the Biosolutionize Agriculture framework, Rovensa Next’s Biostimulation 360° program strengthens nutrient availability and soil‑driven NUE by targeting the root–soil interface with advanced biosolutions. Microbial products such as Wiibio, which stimulate siderophore production, keep essential micronutrients such as iron and phosphorus accessible for longer, reducing nutrient lock‑up and mitigating losses through leaching. Complementary solutions, including Humifirst, Humistar WG, and Turbo Root WG, based on high‑quality humic and fulvic acids, improve soil structure, organic matter mineralization, and cation exchange capacity. These effects boost root biomass, maximize nutrient uptake efficiency, and enhance the long‑term biological fertility of the soil, which are key to sustainable nutrient cycling and regenerative agricultural systems.
Top Rovensa Next products that enhance nutrient availability
Biological nitrogen fixation
- Azzofix & Atmo – improving natural nitrogen supply
Two key inoculants participate in biological nitrogen fixation:
- Atmo inoculates soybeans with Bradyrhizobium japonicum, enabling crops to replace synthetic nitrogen through full symbiotic fixation. In multi‑location trials conducted by Embrapa, soybean yields increased by 8.4% when seeds were only inoculated with Bradyrhizobium.
- Azzofix contains Azospirillum brasilense strains AbV5 and AbV6. When used in co‑inoculation alongside Bradyrhizobium, it further enhances nodulation, root architecture, and early metabolic activity. Embrapa recorded up to 16.1% yield increases with this co‑inoculation strategy.
Why this matters
Biological nitrogen fixation reduces dependence on synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, improves the biological balance of soil, lowers production costs, and boosts sustainability in soybean and corn systems.
Phosphorus solubilization
- Phós’UP – unlocking fixed soil phosphorus
Phosphorus is one of the most limiting nutrients in Brazilian soils due to extremely high fixation rates. Phós’UP addresses this challenge using the Pseudomonas fluorescens BR14810 bacterium, a strain capable of solubilizing fixed soil phosphorus, increasing availability for plant uptake.
In field trials (2020–2021 soybean harvest), Phós’UP increased soybean yields by up to 8.7 additional bags per hectare, confirming its strong contribution to phosphorus use efficiency.
Why this matters
Increasing phosphorus availability directly impacts energy metabolism, flowering, grain formation, and early vigor, which are critical factors in high‑yield environments.

| Product | Mode of Action | Proven Performance Data |
|---|---|---|
| Atmo | Bradyrhizobium japonicum – Biological N fixation | +8.4% yield increase in soybeans (Embrapa) |
| Azzofix | Azospirillum brasilense AbV5 & AbV6 – Co‑inoculation enhancer | +16.1% yield increase when combined with Bradyrhizobium (Embrapa) |
| Phós’UP | Pseudomonas fluorescens BR14810 – P solubilization | +8.7 bags/ha soybean yield increase (field trials 2020–2021) |
Rhizosphere activation
- Phylgreen & Ruter AA – stimulating root activity and nutrient absorption
Phylgreen, a seaweed‑derived biostimulant, helps crops maintain nutrient uptake even under abiotic stress. Trials have shown:
- +33–90% increase in fruit number and weight
- +15–25% yield increase across multiple crops
- +37% performance improvement in broadacre systems
Ruter AA complements this by promoting vigorous vegetative and root growth, thus strengthening the root–soil interface where most nutrient exchange occurs.
- It increases crop yield by up to +18% across multiple crops.
- It boosts root development, with results including +21% longer root systems in broad‑acre crops such as oilseed rape.
- It improves crop quality parameters, including a 7.4% increase in thousand‑seed weight (TSW) in wheat.
Why this matters
Active roots mean better nutrient capture, higher metabolic efficiency, and greater resilience during stress periods.
Soil structure & organic matter transformation
- Humistar WG, Humifirst, Turbo Root WG & Transformer
Humic‑based products such as Humistar WG and Humifirst improve soil porosity, water infiltration, and macroelement mobility. They also stimulate microbial activity, accelerating organic matter mineralization, and boosting nutrient release.
Transformer further enhances physical soil conditions by improving infiltration, water retention, and nutrient availability.
Humifirst® enhances nutrient use efficiency (NUE) because it enables the crop to deliver higher yields and larger commercial calibers without increasing fertilization rates.
Official McCain trials (2017–2020, 18 field sites) demonstrated:
- +5% increase in commercial yield (≥35 mm)
- +2.2 t/ha absolute yield gain
- 83% consistency across sites (15 out of 18 fields)
- +4% increase in large-caliber tubers
- +7% yield increase under irrigation
- Source: McCain Alimentation SAS – Technical Communication Humifirst® (2017–2020).
Why this matters
Healthy soil structure increases nutrient persistence, reduces leaching, and supports a more efficient root system.
Nutrient mobility & translocation
- Delfan Plus, Vegenergy, Calitech
Amino‑acid‑based biostimulants such as Delfan Plus and Vegenergy enhance the mobility of key elements including calcium and boron, especially under stress.
Calitech improves fruit quality and calcium‑related firmness.
Vegenergy delivers a +19.3% yield increase in tomatoes, a +13.6% rise in fruit count, and a 17% reduction in bitter pit in apples.
- Trials conducted at the Polytechnic University of Madrid (2017–2018) under water‑stress conditions showed that Vegenergy increased tomato yield by 19.3%.
- The same study reported a 13.6% rise in fruit count, confirming improved reproductive efficiency despite reduced water availability.
- In apples, Vegenergy reduced bitter pit incidence by 17% when combined with calcium, demonstrating enhanced calcium mobility and fruit quality.
- These results collectively indicate that Vegenergy strengthens nutrient use efficiency (NUE) by enabling crops to convert available nutrients into higher yields and better fruit quality under abiotic stress.
Optimized cell structure
Barrier is a cell‑fortifying technology designed to enhance the physical resistance of plants. It reinforces the structural and functional integrity of plant cells, helping them stay hydrated, protected, and metabolically stable under environmental stress. Its mode of action supports stronger tissue that can better withstand adverse conditions.
Key effects of Barrier linked to optimized cell structure
- Enhances cellular hydration and helps plants retain water under stress.
- Optimizes cell‑wall structure resulting in thicker, more robust stems.
- Strengthens overall cell integrity, contributing to more stable tissue and improved fruit quality.
- Reduces electrolyte leakage and minimizes cellular damage.
- Supports longer shelf life and ensures better storability, driven by healthier, more durable cells.
- End result: greater vigor, improved yield potential, and higher overall benefit for the crop.
Nutrient use efficiency (NUE) enhancement
- Amifol K, ArmoniKa, Armonika Neo Delfan Plus & Final K
Products such as ArmoniKa Neo and Amifol K improve early nutrient uptake and fruit fill, while Final K uses anti‑blocking agents to maximize potassium efficiency under challenging soil conditions.
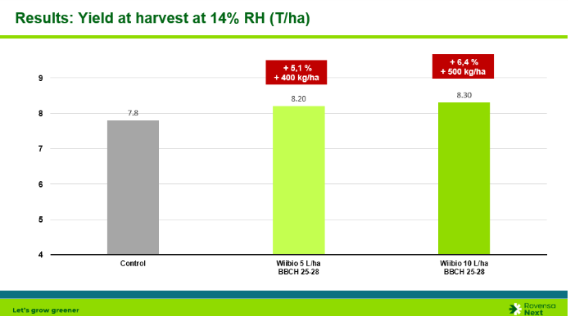
Wiibio: a complete biological soil enhancer
What does Wiibio do?
- It enhances soil microbial diversity and rhizosphere activity.
- It stimulates siderophore production, improving iron and phosphorus uptake.
- It unblocks immobilized phosphorus.
- It boosts mineralization processes and nutrient release.
- It strengthens root nutrient absorption and overall nutrient use efficiency.
Proven effects
Wiibio has been shown to increase iron and phosphorus availability through siderophore production and improve root absorption efficiency, contributing meaningfully to overall NUE.
Why this matters
Wiibio connects soil regeneration to high‑performance nutrition. This is particularly necessary in degraded and low‑fertility soils.
Image 3. Key parameters of the 2025 winter wheat trial conducted in Sietow, Germany.


Biocontrol as a functional enabler of nutrient efficiency
Biocontrol products play a complementary role in Rovensa Next’s biosolutions portfolio by helping to preserve the biological and physiological conditions required for efficient nutrient use.
Microbial biocontrol agents, such as selected Bacillus, Trichoderma and other beneficial microorganisms, operate through competitive exclusion, enzymatic activity, and stimulation of plant defense responses. These mechanisms reduce root damage caused by soil-borne pathogens and nematodes, enabling crops to maintain functional root systems and stable nutrient uptake under biotic stress.
In this context, biocontrol solutions do not replace fertilizers or biofertilizers. Instead, they protect the return on nutrient investment, contributing to resilient, low-input cropping systems.
Adjuvants as efficiency multipliers: maximizing the performance of applied inputs
The effectiveness of crop nutrition and biosolutions is not determined solely by product formulation, but also by how efficiently inputs are delivered to the plant. Spray losses, poor wetting, limited retention, and suboptimal uptake reduce the functional availability of nutrients and biostimulants, increasing waste and variability in field performance.
Advanced adjuvants play a critical role by optimizing spray solution behavior, improving droplet spreading, adhesion, and penetration on the leaf surface. Adjuvants help ensure that applied inputs reach their biological target more consistently by enhancing the physical efficiency of nutrient and biosolution delivery.
In this way, adjuvants such as Transformer act as efficiency multipliers, supporting nutrient availability and nutrient use efficiency indirectly by reducing losses and improving uptake of existing applications, without adding nutrients or biological actives.
Conclusion
Nutrient availability and nutrient use efficiency (NUE) are the cornerstones of truly sustainable, high‑performance agriculture. Rovensa Next’s science‑driven biosolutions help growers to activate soil biology, increase nutrient efficiency, reduce synthetic inputs, and maintain or increase crop productivity, which are all key elements of regenerative agriculture and sustainable crop nutrition.
The future of agriculture is biologically driven, resource‑efficient, and resilient, and the biosolutions needed to achieve it are already here.















